Describe How Enzymes Are Used to Activate Toxins in Plant
Endocannabinoid receptors Special receptors that endocannabinoids bind to as a way of. Lysosomes fuse with the phagosome releasing enzymes into.
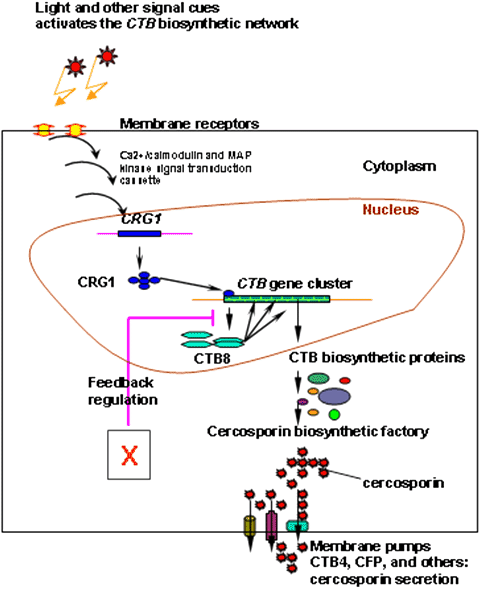
Cercosporin A Photoactivated Toxin In Plant Disease
Host plant defenses against insects.

. Known darkening of apples pears and the other fruits is due to this reaction. Toxins damage enzymes and thus undermine countless bodily functionsinhibiting the production of hemoglobin in the blood for example or. Fruits and vegetables are commonly consumed in their raw natural form.
One example is leukocidins a group of enzymes that destroy white blood cells. Pancreatic enzymes whether produced by the body or provided as a dietary supplement only work in the small intestine. What term is used to describe enzymes which work within the cell produces them.
Enzymes help in this process by unwinding the DNA coils and copying the information. This enzyme breaks down peptides into free amino acids that can be absorbed by the intestinal wall. The membrane folds inwards.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase catalysing the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A. Which pigments are responsible for all the yellows reds and oranges of plants and vegetables. It encode a enzyme involved in tabtoxin biosynthesis.
Defense Responses Against Pathogens. The six kinds of enzymes are hydrolases oxidoreductases lyases transferases ligases and isomerases. And can be used for any number of reasons including transforming grey water for use in the garden or.
Certain cytochrome P450 enzymes are critical in metabolizing polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFAs to biologically active intercellular cell signaling molecules eicosanoids andor metabolize biologically active metabolites of the PUFA to less active or inactive products. This alleviates the overarching issue with animal-based enzymes by preserving the integrity of the enzymes themselves. Used for bioremediation to break toxic chemicals down into non-toxic ones.
Protein Proteins have diverse role in the cellular reactions as enzymes or as structural materials in membranes and cell wall Enzymes degrading proteins are called Proteases or proteinases or peptidases Proteolytic enzymes produced by most of the pathogens can affect the organisation and functions of host cells. Plant enzymes must have moisture in order to perform their digestive function. Enzymatic action increases levels of NPK nitrogen phosphorus and potassium in the garden.
What do enzymes do. Oxidoreductases These catalyze oxidation and reduction reactions eg. By definition a toxin triggers a destructive process Fig.
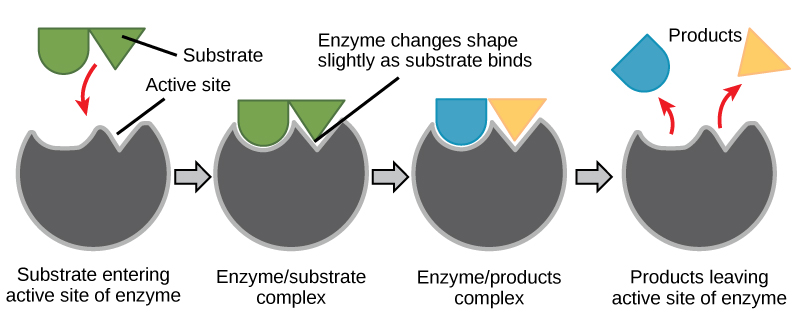
Graph showing lowering of activation energy 2. Fatty acid amidohydrolase FAAH and monoacylglycerol lipase MAGL. An enzymes shape is tied.
Trypsin then activates additional pancreatic enzymes such as carboxypeptidase and chymotrypsin to help break down peptides. Many plants produce secondary metabolites known as. Tab toxin is a dipeptide composed of amino acid threonine and tabtoxinine The toxin as such is not toxic but in the cell it get hydrolysed and release aminoacid tabtoxinine which is toxic Act by inhibiting inactivating the enzyme glutamine synthetase Uncoupling of phosphorylation and photorespiration destroy the.
The neutrophil binds to the pathogen or to opsonin on the pathogen. Additionally enzymes assist in breaking down deleterious chemicals like ammonia. Plants can sense being touched and they can use several strategies to defend against damage caused by herbivores.
Enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction by taking the reactants out of the solution-state desolvation establishing weak bonds between reactants and enzymes and bringing reactant molecules close to one another in the region of active sites. Quite simply digestion is the process of breaking molecules apart with the addition of water hydrolysis. Listed below is the classification of enzymes discussed in detail.
AreMetals that activate enzymes and help bring the active site substrate together. Breaking down food particles during digestion. Liver enzymes the liver breaks down toxins in.
Bacterial toxins are biologic virulence factors that prepare the host for colonization. Trypsin forms when an enzyme secreted by the pancreas is activated by an enzyme in the small intestine. Enzymes are produced naturally in the body and help with important tasks including.
Endocytosis occurs forming a vacuole phagosome that contains the pathogen. Plant defense against herbivory or host-plant resistance HPR describes a range of adaptations evolved by plants which improve their survival and reproduction by reducing the impact of herbivores. This destruction lessens the bodys ability to perform phagocytosis.
However for the reasons outlined above the general consensus is the best sources of enzymes are plant and fungal. Increase in the conc. The two main endocannabinoid enzymes are.
The darkening is caused by the activity of an enzyme either of the peroxidase type or of the phenol oxidase type the difference between which is that the latter can use the oxygen of the air but the former can use only the hydrogen peroxide that is produced by the. I The increased number of enzyme molecules will have more active sites and. Which color is reflected by chlorophyll.
Other bacterial enzymes are hemolysins. Every physiological function depends on enzymes to manufacture molecules produce energy and create cell structures. Toxins poison enzymes so they dont work properly.
Many pathogens produce a series of enzymes to help overcome body defenses and establish themselves in the host. There are two mechanisms by which the linear chains of pectate or pectin are broken hydrolysis and b -elimination the latter giving rise to oligomers which are 45 unsaturated at the non-reducing end. Of the enzyme will increase the rate of reaction catalysed by it provided there is enough conc.
If pathogens breach a plants barriers the plant can respond with secondary metabolites which are often toxic compounds such as glycol cyanide that may harm the pathogen. The body satisfies this need with saliva. Our bodies are enzyme engines.
Usually a very small amount of the enzyme can consume large amount of the substrate. Pectolytic enzymes are classified according to their catalytic activity and this is complicated by the fact that the substrate is heterogeneous. 11-8Toxins can function in multiple ways for example by inhibiting protein synthesis diphtheria toxin activating second messenger pathways Bacillus anthracis edema factor or cholera toxin activating immune responses S.
Plants produce antimicrobial chemicals antimicrobial proteins and antimicrobial enzymes that are able to fight the pathogens. Plants respond to herbivore attack through an intricate and dynamic defense system that includes structural barriers toxic chemicals and attraction of natural enemies of the target pests Fig. 1 9 10 Both defense mechanisms direct and indirect may be present constitutively or induced after damage by the herbivores.

Plant Soil Interactions Nutrient Uptake Learn Science At Scitable
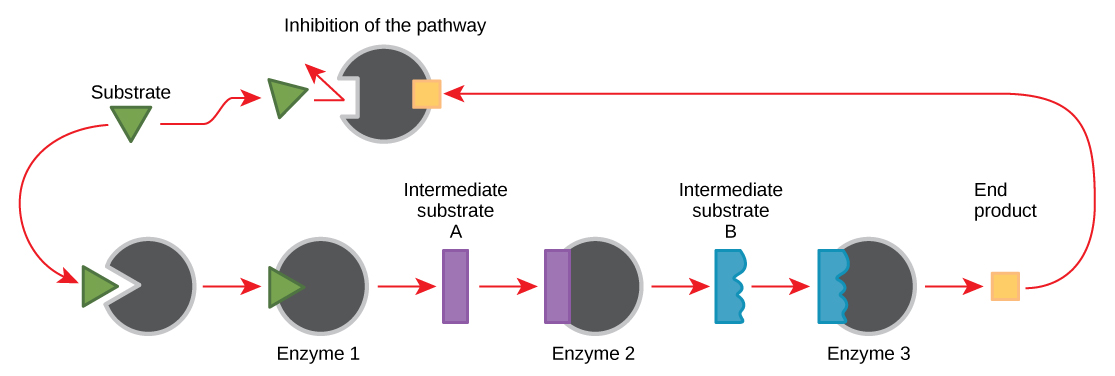
Comments
Post a Comment